Create a table if it does not exist in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is an object-relational database system, which means it can support more complex data types than its competitor MySQL.
Apart from the above differences, when writing queries for PostgreSQL and MySQL or other database systems, the structure tends to be very similar.
Since the backbone of each is the RDBMS, all SQL queries are nearly identical in both instances, with only extensions to each system that they may be created separately.
Creating a table in PostgreSQL is very easy, and in this article, we will discuss all the ways we can write queries to help us create tables.
Use CREATE TABLEthe query to create a table that does not exist in PostgreSQL
One of the most straightforward queries to do this is to write out standard SQL CREATE TABLEas shown below.
Create table if not exists table_one (
u_name varchar(100) not null,
PRIMARY KEY (u_name)
);
This query tends to check if the table does not exist when it is created, and then creates it. If the table already exists, you will receive something like this NOTICE.
Output:
NOTICE: relation "table_one" already exists, skipping
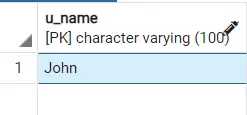
In addition to creating a table, you can also see it in action. You can use INSERTthe command to enter a name and then call SELECTthe operation to output the table.
INSERT into table_one values('John');
select * from table_one;
Output:
Use CREATE 或 REPLACEthe query to create a table that does not exist in PostgreSQL
We can also CREATE 或 REPLACEcreate a function to create a table using the method.
You can use the following code to perform such operation:
CREATE or replace FUNCTION create_user_specific_table()
RETURNS void
LANGUAGE plpgsql AS
$func$
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (SELECT FROM pg_catalog.pg_tables
WHERE tablename = 'table_one') THEN
RAISE NOTICE 'Table table_one already exists.';
ELSE
CREATE TABLE table_one (u_name varchar(50));
END IF;
END
$func$;
SELECT create_user_specific_table();
INSERT INTO table_one (u_name) values('Jonathon');
select * from table_one;
Output:

Now, let's try to analyze how it works. You will see that after the function definition it says CREATEor REPLACE.
CREATE 或 REPLACEPrefers to replace an existing function definition given inside the system, if it is already integrated into the database. So you don't face errors when calling the function again and again.
It can be effectively used for testing instead of deleting the listed function and then recreating it.
$func$are the start and end markers of a function. Inside a function, if the table already exists among the listed tables, it will not be created.
Instead, it sends 表已存在a notification. RAISE NOTICEA function is a function that implements this function.
Different implementations of this function are available for 创建tables . You can also modify this function as it better suits your needs.
If the table does not exist in PostgreSQL, create it using CASEthe statement
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION create_user_specific_table()
RETURNS void
LANGUAGE plpgsql AS
$func$
BEGIN
IF EXISTS (SELECT FROM pg_catalog.pg_tables
WHERE tablename = 'table_one') THEN
RAISE NOTICE 'Table table_one already exists.';
ELSE
CREATE TABLE table_one (u_name varchar(50) not null
, PRIMARY KEY (u_name));
END IF;
END
$func$;
SELECT CASE WHEN (SELECT true::BOOLEAN
FROM pg_catalog.pg_tables
WHERE tablename = 'table_one'
) THEN (SELECT 'success'::void)
ELSE (SELECT create_user_specific_table())
END;
INSERT INTO table_one (u_name) values('Jonathon');
select * from table_one;
The above code is no different from the method given above. It CASEreplaces the simple SELECTquery with a statement.
SELECT CASESame as if elsethe statement. It returns one when tablenameis equal to .table_onetrue
If the table already exists, it returns Success; otherwise, it calls the table creation function. It is very simple and can be effectively used to CASEimplement in notation IF EXISTS.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Killing a process ID in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:191 Category:PostgreSQL
-
Today, we will learn how to kill or stop a running query in the background when working with PostgreSQL database. This may happen if the frontend stops working but a background process is still running. In this case, you may want to kill th
How to install and deploy PostgreSQL as a Docker container
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:50 Category:PostgreSQL
-
PostgreSQL , also known as Postgres, is a leading object-relational database system. It is popular because it is highly compliant with the SQL standard and includes additional features that simplify processing complex data sets at scale. Po
Selecting whether a string contains a substring match in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:186 Category:PostgreSQL
-
Today, we will learn how to find a value in a PostgreSQL string and select it if it matches certain conditions. Suppose you have a string carabc and want to see if it contains a value car . Therefore, you will try to use a function that tel
Add unique constraint after creating table in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:63 Category:PostgreSQL
-
Today we will learn how to add constraints after the rows in a table have been created UNIQUE . The UNIQUE constraint guarantees that the data in a row is unique in that column. So if the column ID exists, all rows will have unique values,
Creating a Schema in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:196 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article will discuss creating schemas in PostgreSQL using SQL queries or psql. CREATE SCHEMA Use the statement to create a pattern in SQL query To create a new schema, execute the following command. CREATE SCHEMA test_schema To view al
Changing User Password in Postgres
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:108 Category:PostgreSQL
-
In this article, we will change the user password in Postgres. Changing User Passwords in Postgres Using Windows Open from the menu or search bar SQL Shell (psql) . Connect to the default database using the default port. If you set it up wi
Changing column types in Postgres
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:91 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article shows how to change a column type to another data type in Postgres. ALTER TABLE To change the column type in Postgres, use the command ALTER TABLE table_name ALTER COLUMN column_name [ SET DATA ] TYPE new_type ; Use 表名 , , 列
Importing SQL files in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:129 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article discusses how to import SQL files in PostgreSQL. psql Import SQL files in PostgreSQL using command To import the SQL file, run the following command: psql - U dbuser - h localhost databasename filename. sql If the file is locat
Difference between timestamps with and without time zone in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:83 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article will discuss the timestamp types in PostgreSQL and show how they differ. Timestamps in PostgreSQL In PostgreSQL, there are two types of timestamps. Timestamp without time zone Timestamp with time zone The first stores the local

