Add unique constraint after creating table in PostgreSQL
Today we will learn how to add constraints after the rows in a table have been created UNIQUE.
The UNIQUE constraint guarantees that the data in a row is unique in that column. So if the column ID exists, all rows will have unique values, rather than duplicate values.
However, even with the constraint, it is possible for more than two rows to have null values.
But what if we forget to add in the column we want UNIQUE? Today, we will look at how to add a unique constraint to the required column after creating the table.
After creating a table in PostgreSQL, use alterthe statement to add a unique constraint
alterThe statement supports inclusion UNIQUE. In our example, we will use an Dogalready created table called .
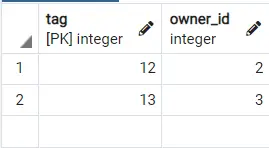
This table has a tagas primary key and a owner_id. owner_idis not set to UNIQUE, because if we insert the following it will work perfectly.
insert into dog values (14, 2);
Output:
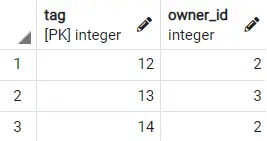
But for now, let's UNIQUEadd the constraint to the column and see what happens owner_idwhen we call .insert
alter table dog add constraint uniq_test UNIQUE (owner_id);
owner_idNow, when we call
for the duplicate in our data insert; (14, 2), this is the error that PostgreSQL will return.
ERROR: duplicate key value violates unique constraint "uniq_test"
DETAIL: Key (owner_id)=(2) already exists.
The constraint we defined as uniq_testis UNIQUEviolated.
UNIQUEBut what
if we already have duplicate values in the table and add the constraint? In this case, ALTERit will fail with the following error:
ERROR: could not create unique index "uniq_test"
DETAIL: Key (owner_id)=(2) is duplicated.
The constraint addition fails because a duplicate key already exists. So how do we fix this?
If you already have a large table and cannot remove duplicate values, you cannot add constraints, even if you use an older query such as the following:
create unique index uniq_test on dog (owner_id);
It will return an DUPLICATEerror.
PostgreSQL does this because if you UNIQUEadd to a column, it means all values must be unique.
If you already have duplicate values, you can't expect the column to be unique; therefore, this is discarded.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Killing a process ID in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:191 Category:PostgreSQL
-
Today, we will learn how to kill or stop a running query in the background when working with PostgreSQL database. This may happen if the frontend stops working but a background process is still running. In this case, you may want to kill th
How to install and deploy PostgreSQL as a Docker container
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:50 Category:PostgreSQL
-
PostgreSQL , also known as Postgres, is a leading object-relational database system. It is popular because it is highly compliant with the SQL standard and includes additional features that simplify processing complex data sets at scale. Po
Selecting whether a string contains a substring match in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:186 Category:PostgreSQL
-
Today, we will learn how to find a value in a PostgreSQL string and select it if it matches certain conditions. Suppose you have a string carabc and want to see if it contains a value car . Therefore, you will try to use a function that tel
Difference between timestamps with and without time zone in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/27 Views:83 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article will discuss the timestamp types in PostgreSQL and show how they differ. Timestamps in PostgreSQL In PostgreSQL, there are two types of timestamps. Timestamp without time zone Timestamp with time zone The first stores the local
Terminate the PostgreSQL connection
Publish Date:2025/04/11 Views:200 Category:PostgreSQL
-
In this article, we will learn how to terminate a PostgreSQL session. Any open connections are run by background processes or tasks, PSQL which may no longer exist despite exiting the user interface or command line tool. Use ps -ef or grep
Single query to rename and change column type in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/11 Views:166 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article describes how to rename a column and change its type in PostgreSQL using only a single query. Renaming and changing column types in MySQL In MySQL , if you want to change the column type and rename it, you can use a simple stat
Joining columns using Select in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/11 Views:177 Category:PostgreSQL
-
MySQL PostgreSQL is an object-relational database system, which means it can support more complex data types than its competitors . Today we will learn how to use SELECT the operator to join the columns of a table. Using operators to || joi
Using CASE in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/11 Views:124 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This article shows how to use the statement in PostgreSQL CASE . CASE How to use the statement in PostgreSQL case Statements are similar to those in general-purpose programming languages if-else . But in SQL, if you want to write IF-ELSE ,
Using NOT IN with subqueries in PostgreSQL
Publish Date:2025/04/11 Views:93 Category:PostgreSQL
-
NOT IN The inverts the result of NOT simply using IN the operator. NOT IN The right side of the operator must have a subquery in which multiple columns are returned to check whether the expression matches the data. NOT IN Tends to return tr

