Smoothing Data in Python
Python has a wide range of applications in data analysis and visualization. When we analyze massive datasets with many observations, we may encounter situations where we have to smooth out the curves on a graph to study the final plot more closely. We will discuss how to achieve this in Python using different methods.
scipy.signal.savgol_filter()Smoothing data in Python using the method
The Savitzky-Golay filter is a digital filter that uses data points to smooth a graph. It uses the least squares method to create a small window and apply a polynomial to the data in that window, then uses the polynomial to hypothesize the center point of a particular window. Next, the window is shifted by one data point, and the process is iterated until all neighbors are adjusted relative to each other.
We can scipy.signal.savgol_filter()do this in Python using the function.
Refer to the following example.
import numpy as np
from scipy.signal import savgol_filter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.random(100) * 0.2
yhat = savgol_filter(y, 51, 3)
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.plot(x, yhat, color="green")
plt.show()
Output:

In the above example, we used the filter method to smooth the data to be plotted on the y-axis. We plotted both the original data and the smoothed data so that you can observe the difference.
numpy.convolveSmoothing data in Python using the method
numpy.convolve()Given the discrete linear convolution of two 1D series, we will use this to create a moving average that can filter and smooth the data.
This is not considered a good approach.
For example,
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.random(100) * 0.8
def smooth(y, box_pts):
box = np.ones(box_pts) / box_pts
y_smooth = np.convolve(y, box, mode="same")
return y_smooth
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.plot(x, smooth(y, 3))
plt.plot(x, smooth(y, 19))
Output:
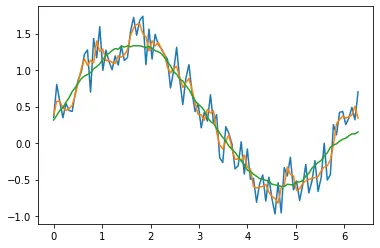
In the above example, we have plotted two moving averages with time increments of 3 and 19. We have plotted them in the graph.
We can also use other methods to calculate moving averages.
statsmodels.kernel_regressionSmoothing Data in Python
Kernel regression computes the conditional mean E[y|X], where y = g(X) + eand fits the model. It can be used to smooth data based on control variables.
To do this, we have to use the function statsmodelsfrom the module KernelReg().
For example,
from statsmodels.nonparametric.kernel_regression import KernelReg
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x) + np.random.random(100) * 0.2
kr = KernelReg(y, x, "c")
plt.plot(x, y, "+")
y_pred, y_std = kr.fit(x)
plt.plot(x, y_pred)
plt.show()
Output:
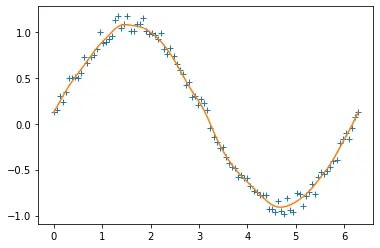
Note that this method produces good results but is considered very slow. We can also use Fourier transform, but it only works for periodic data.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Convert a list to a set in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:144 Category:Python
-
This tutorial demonstrates how to convert a list to a set in Python. Difference between List and Set Lists and sets are standard Python data types that store values in sequence. Python list stores comma separated values between
Remove the first element from a list in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:172 Category:Python
-
This tutorial will discuss different ways on how to remove the first element from a list. pop() Remove the first element from a list using the pop() Method can remove an element from a specific index. We have to specify the index from which
Convert a list to lowercase in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:112 Category:Python
-
Lists can be used to store multiple items in a single variable. In Python, we can create a list of strings by enclosing the different elements in the list in single or double quotes. This tutorial demonstrates how to convert a list of strin
Remove all occurrences of an element from a Python list
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:69 Category:Python
-
In Python, lists allow the same element to appear multiple times. Even though the value of an element may be the same as other elements, each element will have a different index. Using these index numbers, you can easily access any element
Convert hex to bytes in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:101 Category:Python
-
Hexadecimal, often abbreviated to hex, uses 16 symbols (0-9, a-f) to represent values, in contrast to the decimal system's 10. For example, 1000 in decimal is 3E8 in hexadecimal. Being proficient in dealing with hexadecimal is essential for
b in front of string in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:53 Category:Python
-
This tutorial will discuss the statement in Python b" . b" Using the statement in Python b" The notation is used to specify strings in Python bytes . In contrast to regular strings with ASCII characters, bytes a string is an array of byte v
How to Convert Integer to Binary in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:130 Category:Python
-
This tutorial explains how to convert an integer to binary in Python. This tutorial also lists some sample codes to illustrate different ways of converting from int to binary in Python. bin() Convert Int to Binary in Python using In Python,
How to convert an integer to bytes
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:77 Category:Python
-
Converting an integer int to a byte bytes is the inverse of bytes converting a byte to an integer . Most of the to methods int described in this article are the inverse of the to methods. int bytes bytes int Generic method for converting in
How to convert bytes to int in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/08 Views:111 Category:Python
-
Bytes The data type has a numerical range of 0~255 (0x00~0xFF). A byte has 8 bits of data, that's why its maximum value is 0xFF. In some cases, you need to convert a byte or byte array to an integer for further data processing. Let's see ho

