Reading binary files in Python
The program or internal processor interprets the binary file. It contains bytes as content. When we read a binary file, an bytesobject of type is returned.
open()Read a binary file
using the function in Python
In Python, we have open()the openFile function, which is used to create a file object. Pass the path of the file to the function and open the file in a specific mode, which is read mode by default. When we open a binary file, we have to specify bthe openFile parameter while opening such a file in read, write or append mode. In this tutorial, we will deal with the binary read mode - READ_MODE rb.
In the following code, we will read a binary file and print a character from the file.
with open("sample.bin", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
print(data[2])
Output:
83
If we print the individual characters then we can look at the integers.
Python has a structpackage called that has many methods for working with binary data stored in files, databases, and more.
struct.unpack()Used to read packed data in a specified format layout. This layout is used when packing and unpacking data and is specified using format characters. These format characters and their sizes are shown below.
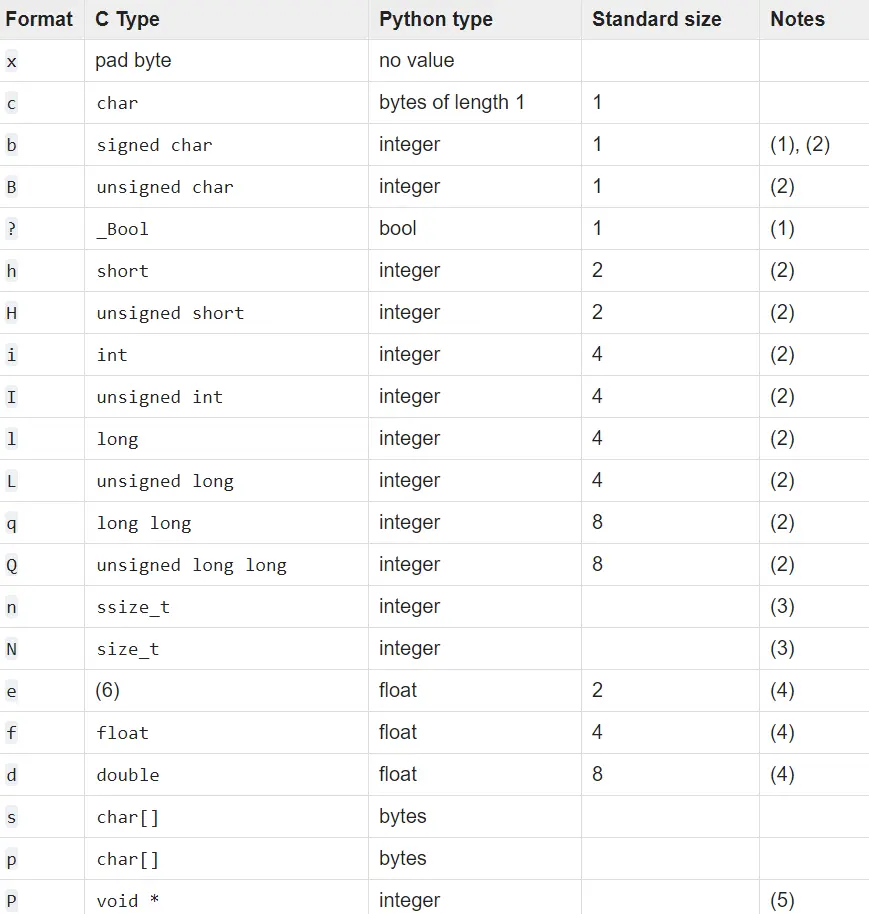
Note that struct.unpack()functions always return a tuple.
import struct
with open("sample.bin", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
unpack_result = struct.unpack("hhl", data[0:8])
print(unpack_result)
Output:
(1280, 27731, 7037801)
Here, hhlshort, short, long int is represented as the data format layout, which we can see in the output. That is why the unpacked buffer is only 8 bytes, because the size of the format layout is 8 (2+2+4).
pathlib.PathReading binary files
with Python
We can also use the method in the class pathlibin the library to read the file in byte mode and then interpret the data using the function as described earlier.Pathread_bytes()struct.unpack()
from pathlib import Path
import struct
data = Path("sample.bin").read_bytes()
multiple = struct.unpack("ii", data[:8])
print(multiple)
Output:
(1817380096, 7037801)
numpy.fromfile()Read a binary file
using the function in Python
NumPyThere is another interesting method provided in the module. Using fromfile()the function in this module, we can dtype()read binary data from a file after specifying the format data using the function. This is considered as a fast method. The following code shows how to implement this functionality.
import numpy as np
with open("sample.bin") as f:
rectype = np.dtype(np.int32)
bdata = np.fromfile(f, dtype=rectype)
print(bdata)
Output:
[1817380096 7037801]
Here, we specify the format type as a 32-bit integer and use fromfile()the function to extract the data.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Read the first line of a file in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:192 Category:Python
-
In Python, we have built-in functions to handle different file operations. A text file contains a sequence of strings where each line \n is terminated by a newline character. In this tutorial, we will learn how to read the first line of a t
Writing bytes to a file in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:193 Category:Python
-
In this tutorial, we will look at how to write bytes to a binary file in Python. Binary files contain strings of type bytes. When we read a binary file, an object of type bytes is returned. In Python, bytes are represented by hexadecimal nu
Python get file name without extension from path
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:81 Category:Python
-
This tutorial will demonstrate various ways to get the file name without extension from a file path in Python. Suppose our goal is to get the file name from a list of file paths that are in the form of strings, such as from the path Desktop
Calculate the time difference between two time strings in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:182 Category:Python
-
Sometimes we have to deal with date and time related problems in programming. In Python, date and time are not data types themselves. Despite this, Python provides a large number of functions and libraries to help deal with such problems. O
Optional parameters in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:151 Category:Python
-
In Python, there is something called default arguments. It is also called optional parameters or optional arguments in python. Parameters refer to the inputs of a function. Functions with multiple optional parameters in Python Whenever you
Writing floating point numbers to a file in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:91 Category:Python
-
Python makes writing data to a file a seamless task. The data is written to the file in the form of strings. In this article, you will learn how to write float values to a file in Python. Writing floating point numbers to a file in Py
How to read specific lines from a file in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:181 Category:Python
-
A common way to read files in Python is to read the file completely and then process specific lines. Reading files in Python is fast, for example, it takes about 0.67 seconds to write a 100MiB file. However, if the file size exceeds 100MB,
Calculating the arithmetic mean in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:190 Category:Python
-
The term arithmetic mean is the average of the numbers. The mathematical formula to determine the arithmetic mean is to divide the sum of the numbers by the count. It is determined in Python in the following way. Use mathematical formulas.
Cosine Similarity in Python
Publish Date:2025/05/05 Views:81 Category:Python
-
Cosine similarity measures the similarity between two lists of vectors by calculating the cosine angle between them. If you consider the cosine function, it has a value of 1 at 0 degrees and -1 at 180 degrees. This means that for two overla

