Python 中 IndexError: list assignment index out of range 错误解决
在 Python 中,当您尝试访问甚至不存在的列表的索引时,会引发 IndexError: list assignment index out of range。 索引是可迭代对象(如字符串、列表或数组)中值的位置。
在本文中,我们将学习如何修复 Python 中的 Index Error list assignment index out-of-range 错误。
Python IndexError:列表分配索引超出范围
让我们看一个错误的例子来理解和解决它。
代码示例:
# error program --> IndexError: list assignment index out of range
i = [7,9,8,3,7,0] # index range (0-5)
j = [1,2,3] # index range (0-3)
print(i,"\n",j)
print(f"\nLength of i = {len(i)}\nLength of j = {len(j)}" )
print(f"\nValue at index {1} of list i and j are {i[1]} and {j[1]}")
print(f"\nValue at index {3} of list i and j are {i[3]} and {j[3]}") # error because index 3 isn't available in list j
输出:
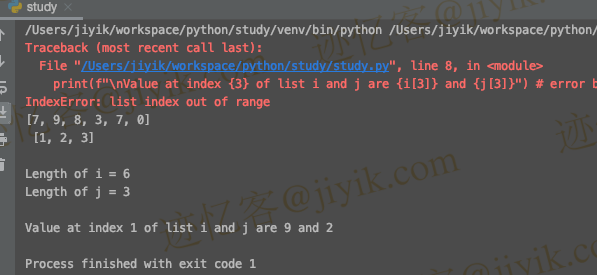
上面代码中 IndexError: list assignment index out of range 背后的原因是我们试图访问索引 3 处的值,这在列表 j 中不可用。
修复 Python 中的 IndexError: list assignment index out of range
要修复此错误,我们需要调整此案例列表中可迭代对象的索引。 假设我们有两个列表,你想用列表 b 替换列表 a。
代码示例:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
b[k] = l # indexError --> because the length of b is 0
k += 1
print(f"{a}\n{a}")
输出:
IndexError: list assignment index out of range
您不能为列表 b 赋值,因为它的长度为 0,并且您试图在第 k 个索引 b[k] = I 处添加值,因此它会引发索引错误。 您可以使用 append() 和 insert() 修复它。
修复 IndexError: list assignment index out of range 使用 append() 函数
append() 函数在列表末尾添加项目(值、字符串、对象等)。 这很有帮助,因为您不必处理索引问题。
代码示例:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
# use append to add values at the end of the list
j.append(l)
k += 1
print(f"List a: {a}\nList b: {a}")
输出:
List a: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
List b: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
修复 IndexError: list assignment index out of range 使用 insert() 函数
insert() 函数可以直接将值插入到列表中的第 k 个位置。 它有两个参数,insert(index, value)。
代码示例:
a = [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13]
b = []
k = 0
for l in a:
# use insert to replace list a into b
j.insert(k, l)
k += 1
print(f"List a: {a}\nList b: {a}")
输出:
List a: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
List b: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
除了上述两种解决方案之外,如果你想像对待其他语言中的普通数组一样对待 Python 列表,你可以使用 None 值预定义你的列表大小。
代码示例:
a = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
b = [None] * len(i)
print(f'Length of a: {len(a)}')
print(f'Length of b: {len(b)}')
print(f"\n{a}\n{b}")
输出:
Length of a: 6
Length of b: 6
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
[None, None, None, None, None, None]
一旦你用虚拟值 None 定义了你的列表,你就可以相应地使用它。
总结
可能有更多的手动技术和逻辑来处理 IndexError:Python 中的列表分配索引超出范围。 本文概述了两个常见的列表函数,它们可以帮助我们在替换两个列表时帮助我们处理 Python 中的索引错误。
我们还讨论了预定义列表并将其视为类似于其他编程语言数组的数组的替代解决方案。
相关文章
Python pandas.pivot_table() 函数
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:82 分类:Python
-
Python Pandas pivot_table()函数通过对数据进行汇总,避免了数据的重复。
在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列的日期时间转换为字符串
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:894 分类:Python
-
了解如何在 Python 中将 Pandas 系列日期时间转换为字符串
在 Python Pandas 中使用 str.split 将字符串拆分为两个列表列
发布时间:2024/04/24 浏览次数:1124 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍如何使用 pandas str.split() 函数将字符串拆分为两个列表列。
在 Pandas 中将 Timedelta 转换为 Int
发布时间:2024/04/23 浏览次数:231 分类:Python
-
可以使用 Pandas 中的 dt 属性将 timedelta 转换为整数。
Python 中的 Pandas 插入方法
发布时间:2024/04/23 浏览次数:112 分类:Python
-
本教程介绍了如何在 Pandas DataFrame 中使用 insert 方法在 DataFrame 中插入一列。
使用 Python 将 Pandas DataFrame 保存为 HTML
发布时间:2024/04/21 浏览次数:106 分类:Python
-
本教程演示如何将 Pandas DataFrame 转换为 Python 中的 HTML 表格。
如何将 Python 字典转换为 Pandas DataFrame
发布时间:2024/04/20 浏览次数:73 分类:Python
-
本教程演示如何将 python 字典转换为 Pandas DataFrame,例如使用 Pandas DataFrame 构造函数或 from_dict 方法。
如何在 Pandas 中将 DataFrame 列转换为日期时间
发布时间:2024/04/20 浏览次数:101 分类:Python
-
本文介绍如何将 Pandas DataFrame 列转换为 Python 日期时间。

