Using pipelines in MongoDB query operations
This article teaches you how to use pipelines in MongoDB's lookupAggregation Pipeline operator. Before proceeding, you must have enough knowledge about the aggregation pipeline and the Aggregation Pipeline operator to understand the use of pipelines in the Aggregation Pipeline operator $lookupwhen working with MongoDB .$lookup
If you already understand these concepts, you can quickly move on to the last two code examples in this tutorial.
What is an aggregation pipeline
It is the process of collecting data and returning calculation results. This process collects data from different documents, groups them according to specified conditions, and performs various operations on the grouped data.
For example, average, sum, maximum, and minimum. It is just like a SQL aggregate function.
In MongoDB, we can use aggregation in the following three ways.
You can also read here for a deeper understanding of the aggregation pipeline.
$lookupWhat are operators
in MongoDB ?
This operator is used to perform a left outer join to merge data from one document to another document in the same database. It filters the documents from the joined collection for further processing.
We can also use this operator to add extra fields to existing documents.
$lookupThe operator adds a new array attribute (field) whose values (elements) match the documents in the joined collection. These transformed documents are then passed to the next stage.
$lookupThe operator has three different syntaxes that we can use based on the project requirement. This tutorial uses $lookupthe syntax to represent it Join conditions & Subqueries on the Joined Collection.
To practice the example code, let's prepare a sample collection with data.
Sample code:
db.createCollection('collection1');
db.createCollection('collection2');
db.collection1.insertMany([
{"shopId": "001", "shopPosId": "001", "description": "description for 001"},
{"shopId": "002", "description": "description for 002"},
{"shopId": "003", "shopPosId": "003", "description": "description for 003"},
{"shopId": "004", "description": "description for 004"}
]);
db.collection2.insertMany([
{"shopId": "001", "shopPosId": "0078", "clientUid": "474192"},
{"shopId": "002", "shopPosId": "0012", "clientUid": "474193"},
{"shopId": "003", "shopPosId": "0034", "clientUid": "474194"},
{"shopId": "004", "shopPosId": "0056", "clientUid": "474195"}
]);
Now, we can execute the following command to see the documents inserted in each collection.
db.collection1.find();
db.collection2.find();
Use pipelining in $lookupthe operator to concatenate conditions in MongoDB
To understand how to $lookupuse pipes with the operator, let's join documents from two collections where collection1.shopIdis equal to collection2.shopIdand collection1does not contain shopPosIdthe field.
Only those documents from both collections that satisfy these two conditions will be joined. Refer to the sample code given below.
Sample code:
db.collection2.aggregate([
{
"$lookup": {
"from": "collection1",
"let": { "shopId": "$shopId" },
"pipeline": [{
"$match": {
"$and": [
{"$expr": {"$eq": ['$shopId', '$$shopId'] }},
{ "shopPosId": { "$exists": false } }
]
}
}],
"as": "shopDescription"
}
}
]).pretty();
Output:
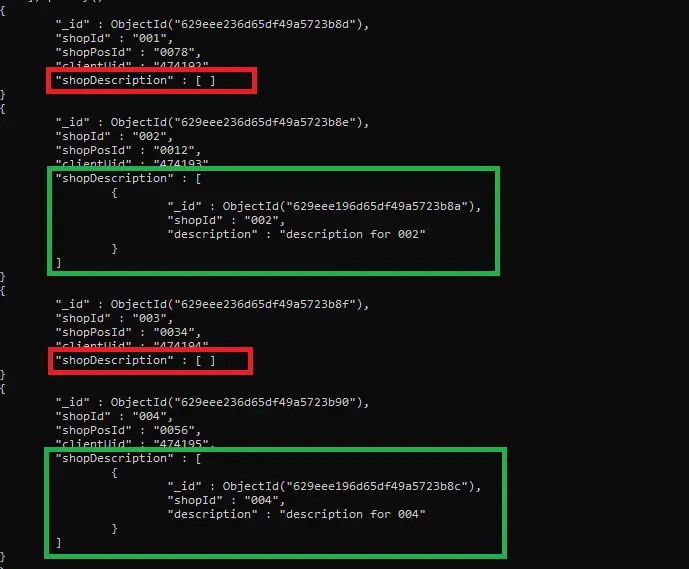
Did you observe the output given above carefully? Only those documents are joined from both the collections that satisfy both the conditions in the pipeline ( collection1.shopIdequals collection2.shopId, and collection1does not contain shopPosIdfields).
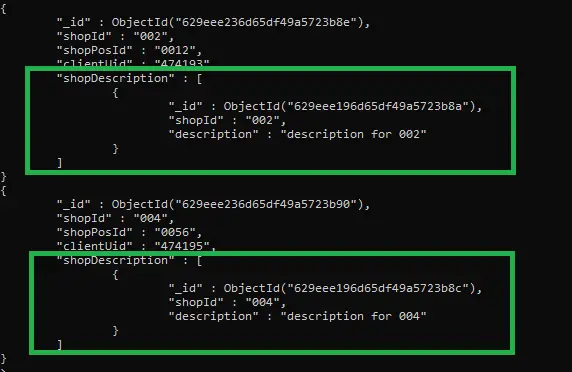
Additionally, those documents that do not meet these conditions have an shopDescriptionempty array called (see the red box in the results above). We can only display those shopDescriptionresult documents that have a non-empty array (see the query below).
Sample code:
db.collection2.aggregate([
{
"$lookup": {
"from": "collection1",
"let": { "shopId": "$shopId" },
"pipeline": [{
"$match": {
"$and": [
{"$expr": {"$eq": ['$shopId', '$$shopId'] }},
{ "shopPosId": { "$exists": false } }
]
}
}],
"as": "shopDescription"
}
},
{
"$match":{
"shopDescription": { $exists: true, $not: {$size: 0} }
}
}
]).pretty();
Output:
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
List all collections in MongoDB Shell
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:156 Category:MongoDB
-
When using MongoDB , there are several ways to list the collections in the database. This article will discuss four different ways to get a list of collections in a MongoDB database. These methods are as follows: show collections List all c
Querying for non-null values in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:139 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB article will explain how to query for non-null values in MongoDB. To query for non-null values, you can use $ne the operator and $eq the operator and then specify the desired value to query. This article shows the readers
Shutting down with code:100 error in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:53 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB tutorial will teach you to fix the error on different operating systems shutting down with code:100 . It will also talk about the root cause of why this issue occurs. shutting down with code:100 Errors in MongoDB As we all know
SELECT COUNT GROUP BY in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:74 Category:MongoDB
-
In this article, we will discuss the functions in MongoDB. Also, we will point out the aggregation functions in detail. We will explain in detail the different ways to count and sort multiple and single fields of Group in MongoDB. Operation
Differences between MongoDB and Mongoose
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:80 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB article will discuss the differences between MongoDB and Mongoose. Unfortunately, most beginners tend to confuse these two concepts when they start developing applications and use MongoDB as their backend. MongoDB has its own s
Install MongoDB using Homebrew
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:161 Category:MongoDB
-
MongoDB is a well-known unstructured database management system that can handle large amounts of data. It is a document-oriented database system and belongs to the NoSQL family (non-SQL). Data and records are stored as documents that look a
Create a MongoDB dump of the database
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:62 Category:MongoDB
-
In this MongoDB article, you’ll get a walkthrough of Mongodump and Mongorestore , how to use them, and some simple examples of backing up and restoring your collections using both tools. mongodump Commands in MongoDB Mongodump is a tool t
Get the size of the database in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:88 Category:MongoDB
-
When working in MongoDB, do you know the size of your database? Today, we will learn how to get the size of a database in MongoDB using show dbs the command and the method. db.stats() Get the size of the database in MongoDB We can show dbs;
Grouping values by multiple fields with MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:99 Category:MongoDB
-
MongoDB Group by Multiple Fields is used to group values by multiple fields using various methods. One of the most efficient ways to group various fields present in MongoDB documents is by using $group the operator, which helps in per

