Update multiple documents in MongoDB
This article will discuss how to efficiently update multiple documents in MongoDB.
updateMany()Methods
in MongoDB
Using the update method in MongoDB db.collection.updateMany(), you can update multiple documents in a collection. This method changes all the collection documents that match the specified filter.
Here are some considerations when using this method.
grammar:
db.collection.updateMany(
<filter>,
<update>,
{
upsert: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
arrayFilters: [ <filterdocument1>, <filterdocument2>... ],
hint: <document|string>
}
)
parameter:
-
filter: This is the first parameter of the method. It specifies the selection criteria for the update.This parameter is of type Document. If it contains an empty record,
{}then this method will update all documents of the collection with the updated document. -
update: This is the second parameter of the method. This parameter type is either a document or a pipe and it contains the changes to the document.It can be an updated document (containing edit operator expressions) or an aggregation pipeline (containing only aggregation steps, such as
$addFields,$projectand$replaceRoot).
Optional parameters:
-
upsert: The value of this parameter is true or false. The value of this parameter is assumed to be truetrue.This procedure will update all documents that meet the criteria specified in the scheme. If any document in the collection does not fit the provided filter, this method will enter the new document (i.e. the updated document) in the collection.
The default value for this option is
false, which is a boolean value. -
writeConcern: This is the only option when you do not want to use the default write concern. This option has parameter type documentation. -
collation: It describes how the collation will be used in the operation. It also allows the user to establish language-specific string comparison standards, such as lowercase and accent mark rules.This option has a parameter type for the documentation.
-
arrayFilters: This is an array of filter documents that tells you which array elements you want to change for array field updates. This parameter has an array type. -
hint: It is a document or field indicating the filter will be used for the index that supports it. It can accept either an index specification document or an index name string, and it will return an error if you choose an index that does not exist. -
Return: This method will return a boolean value oftrue(ifwriteconcernenabled) orfalse(ifwriteconcerndisabled) for the document,matchedCounta value of for the number of matching documents, a value of for the number of modified records, and a value ofmodifiedCountfor updates to inserted documents ._idupsertedId
$setOperators
in MongoDB
You typically use $setthe operator to form update parameters. It replaces the value of a field with a user-given value.
grammar:
{ $set: { <field1>: <value1>, <field2>: <value2>, ...}}
Assume fielddoes not exist. The operator will then $setcreate a new field with the value provided in the record.
If you use dot notation definition field, for example embededDoc.field,, and it does not exist in the database field, $setthe operator creates the embedded document.
Create a collection to update in MongoDB
You can use the following productscollection called .
db={
"products": [
{
"_id": 1,
"name": "xPhone",
"price": 799,
"specs": {
"ram": 4,
"screen": 6.5,
"cpu": 2.66
},
"color": [
"white",
"black"
],
"storage": [
64,
128,
256
]
},
{
"_id": 2,
"name": "xTablet",
"price": 899,
"specs": {
"ram": 16,
"screen": 9.5,
"cpu": 3.66
},
"color": [
"white",
"black",
"purple"
],
"storage": [
128,
256,
512
]
},
{
"_id": 3,
"name": "SmartTablet",
"price": 899,
"specs": {
"ram": 12,
"screen": 9.7,
"cpu": 3.66
},
"color": [
"blue"
],
"storage": [
16,
64,
128
]
},
{
"_id": 4,
"name": "SmartPad",
"price": 699,
"specs": {
"ram": 8,
"screen": 9.7,
"cpu": 1.66
},
"color": [
"white",
"orange",
"gold",
"gray"
],
"storage": [
128,
256,
1024
]
},
{
"_id": 5,
"name": "SmartPhone",
"price": 599,
"specs": {
"ram": 4,
"screen": 5.7,
"cpu": 1.66
},
"color": [
"white",
"orange",
"gold",
"gray"
],
"storage": [
128,
256
]
}
]
}
updateMany()Update multiple documents in MongoDB
using the method
The following example uses updateMany()the method to update a record when the price field value is 899..
db.products.updateMany(
{ price: 899},
{ $set: { price: 895 }}
)
The input in this query filteris {price: 899},, which specifies the document to be updated. The change to be applied is {$set: { price: 895}}, which assigns the field value to using setthe operator .price895.
Output:
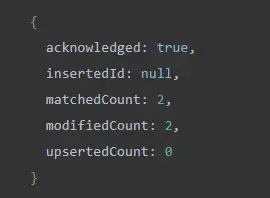
The field in the result document matchedCountindicates the number of matching records, while modifiedCountthe field stores the number of updated documents.
To verify the modification, use find()the method to select the document whose pricefield value is 895,, as shown below:
db.products.find({
price: 895
}, {
name: 1,
price: 1
})
Output:
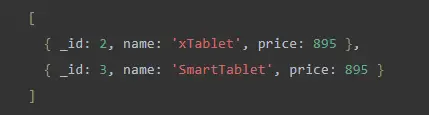
The above image shows that pricethe field value has been updated successfully.
updateMany()Update embedded documents in MongoDB
using the method
The following query uses find()the method to find documents where pricethe value of the field is greater than 700.
db.products.find({
price: { $gt: 700}
}, {
name: 1,
price: 1,
spec: 1
})
Output:
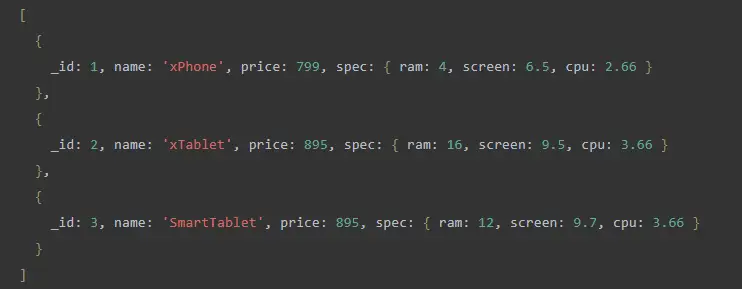
updateMany()The method is used in the embedded document of these documents specto update the values of the ram, screen, and cpufields:
db.products.updateMany({
price: { $gt: 700}
}, {
$set: {
"spec.ram": 32,
"spec.screen": 9.8,
"spec.cpu": 5.66
}
})
Output:
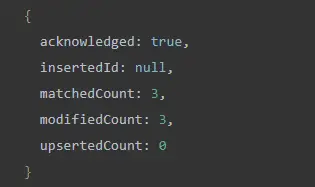
The results in the image show that the three documents were successfully updated.
updateMany()Update array elements in MongoDB
using method
updateMany()The method is used in the following example to update storagethe first and second elements of the document array, where _idare 1, , 2and 3.
db.products.updateMany({
_id: {
$in: [1, 2, 3]
}
}, {
$set: {
"storage.0": 16,
"storage.1": 32
}
})
Output:
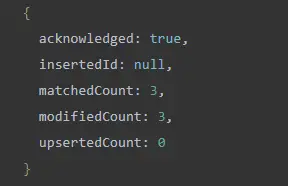
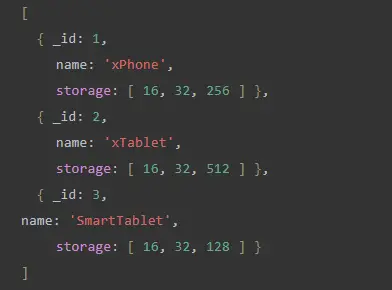
If you productsquery the collection _idfor documents where 1, , 2and , the first and second components of the array have been modified.3storage
db.products.find(
{ _id: { $in: [1,2,3]}},
{ name: 1, storage: 1}
)
Output:
in conclusion
In this tutorial article, you learned how to use updateMany()the Update function to update all records in a collection that meet a condition, and use $setthe Replace operator to replace the value of a field with a specific value.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
List all collections in MongoDB Shell
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:156 Category:MongoDB
-
When using MongoDB , there are several ways to list the collections in the database. This article will discuss four different ways to get a list of collections in a MongoDB database. These methods are as follows: show collections List all c
Querying for non-null values in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:139 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB article will explain how to query for non-null values in MongoDB. To query for non-null values, you can use $ne the operator and $eq the operator and then specify the desired value to query. This article shows the readers
Shutting down with code:100 error in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:53 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB tutorial will teach you to fix the error on different operating systems shutting down with code:100 . It will also talk about the root cause of why this issue occurs. shutting down with code:100 Errors in MongoDB As we all know
SELECT COUNT GROUP BY in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:74 Category:MongoDB
-
In this article, we will discuss the functions in MongoDB. Also, we will point out the aggregation functions in detail. We will explain in detail the different ways to count and sort multiple and single fields of Group in MongoDB. Operation
Differences between MongoDB and Mongoose
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:80 Category:MongoDB
-
This MongoDB article will discuss the differences between MongoDB and Mongoose. Unfortunately, most beginners tend to confuse these two concepts when they start developing applications and use MongoDB as their backend. MongoDB has its own s
Install MongoDB using Homebrew
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:161 Category:MongoDB
-
MongoDB is a well-known unstructured database management system that can handle large amounts of data. It is a document-oriented database system and belongs to the NoSQL family (non-SQL). Data and records are stored as documents that look a
Create a MongoDB dump of the database
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:62 Category:MongoDB
-
In this MongoDB article, you’ll get a walkthrough of Mongodump and Mongorestore , how to use them, and some simple examples of backing up and restoring your collections using both tools. mongodump Commands in MongoDB Mongodump is a tool t
Get the size of the database in MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:88 Category:MongoDB
-
When working in MongoDB, do you know the size of your database? Today, we will learn how to get the size of a database in MongoDB using show dbs the command and the method. db.stats() Get the size of the database in MongoDB We can show dbs;
Grouping values by multiple fields with MongoDB
Publish Date:2025/04/29 Views:99 Category:MongoDB
-
MongoDB Group by Multiple Fields is used to group values by multiple fields using various methods. One of the most efficient ways to group various fields present in MongoDB documents is by using $group the operator, which helps in per

