awk tutorial – 7 awk printing examples
This is the first article in the new awk tutorial series. We will publish several articles on awk in the coming time, which will explain all the features of awk with practical examples.
In this article, let's review the basic awk working methods and 7 practical awk printing examples.
awk introduction and printing operations
awk is a programming language that can easily manipulate structured data and generate formatted reports. Awk stands for the names of its authors, " Aho , Weinberger , and Kernighan ."
Awk is mainly used for pattern scanning and processing. It searches one or more files to see if they contain lines that match the specified pattern, and then performs related operations.
Some key features of awk are:
- awk treats text files as records and fields.
- Like common programming languages, Awk has variables, conditionals, and loops.
- awk has arithmetic and string operators.
- awk can generate formatted reports
awk reads data from a file or from its standard input and outputs to its standard output. awk cannot process non-text files.
语法awk '/search pattern1/ {Actions} /search pattern2/ {Actions}' file
In the above awk syntax:
- The search pattern is a regular expression.
- Actions - statements to be executed.
- There are many modes and operations that can be used in awk.
- file——input file.
- The single quotes around the program are to avoid any special characters in it being interpreted by the shell.
How awk works
awk reads the input file one line at a time.
- For each line, it matches the given patterns in the given order and if there is a match performs the corresponding action.
- If no pattern matches, no action is performed.
- In the above syntax, either the search pattern or the operation is optional, but not both.
- If no search pattern is given, Awk performs the given action on each line of input.
- If no action is given, all lines matching the given pattern are printed, which is the default action.
- Empty brackets without any action do nothing. It does not perform the default print action.
- Each statement in Actions should be separated by a semicolon.
Let us create employee.txt file with the following contents , which will be used in the examples mentioned below.
employee.txt100 Thomas Manager Sales $5,000 200 Jason Developer Technology $5,500 300 Sanjay Sysadmin Technology $7,000 400 Nisha Manager Marketing $9,500 500 Randy DBA Technology $6,000
awk example 1. awk's default behavior
By default, Awk prints each line in a file.
$ awk '{print;}' employee.txt
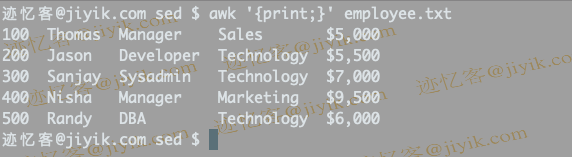
In the above examples no pattern is given. Hence, these operations are applied to all rows.
By default, the action print without any arguments prints the entire line. So it successfully prints all the lines of the file. Action must be enclosed in curly braces.
awk example 2. Print lines matching a pattern
$ awk '/Thomas/
> /Nisha/' employee.txt
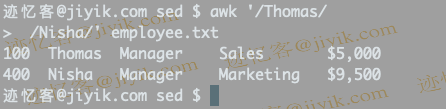
In the above example, it prints all the lines that match "Thomas" or "Nisha". It has two patterns. awk accepts any number of patterns, but each set (pattern and its corresponding action) must be separated by a newline character.
awk example 3. Print only specific fields
awk has many built-in variables. For each record, i.e. line, it by default splits the record separated by whitespace characters and stores it in $nvariables. If the line has 4 words, it will be stored in $1 , $2 , $3, and $4 . $0 represents the entire line. NF is a built-in variable that represents the total number of fields in a record.
$ awk '{print $2,$5;}' employee.txt
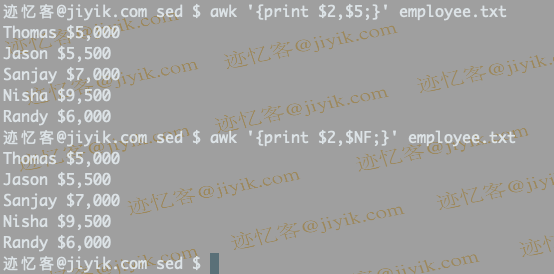
In the above example, $2and $5represent Name and Salary respectively . We can also use $NFto get the salary, where $NFrepresents the last field. In printthe statement, ,is a connector.
awk example 4. Initialization and final operations
There are two important modes in awk, designated by the keywords BEGIN and END .
语法BEGIN { Actions} {ACTION} # Action for everyline in a file END { Actions } # 这里是Awk注释
The actions specified in the BEGIN section will be executed before starting to read lines from the input.
The END action will be executed after the input line has been read and processed.
$ awk 'BEGIN {print "Name\tDesignation\tDepartment\tSalary";}
{print $2,"\t",$3,"\t",$4,"\t",$NF;}
END{print "Report Generated\n--------------";
}' employee.txt
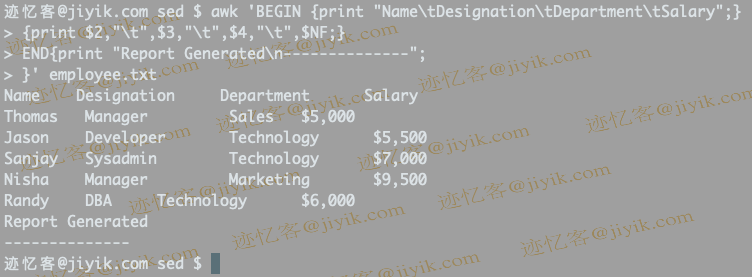
In the above example, it prints the title and the last file of the report.
Awk Example 5. Find employees whose employee id is greater than 200
$ awk '$1 >200' employee.txt
300 Sanjay Sysadmin Technology $7,000
400 Nisha Manager Marketing $9,500
500 Randy DBA Technology $6,000

In the example above, the first field $1is the employee ID. So if $1it is greater than 200, then just do the default print action and print the entire row.
awk Example 6. Printing a list of employees in the technical department
Now the department name is available as the fourth field, so we need to check $4if it matches the string " Technology " and print the line if so.
$ awk '$4 ~/Technology/' employee.txt

operator is ~used to compare with the regular expression. If it matches the default action i.e. print the entire line will be executed.
awk Example 7. Print the number of employees in the technical department
The following example checks if the department is Technology and if so, increments the variable in Action countthat was initialized to zero in the BEGIN section.
$ awk 'BEGIN { count=0;}
$4 ~ /Technology/ { count++; }
END { print "Number of employees in Technology Dept =",count;}' employee.txt

Then at the end of the process, we simply print countthe value of , which gives us the number of employees in the Technology department.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Restart PostgreSQL in Ubuntu 18.04
Publish Date:2025/04/09 Views:72 Category:PostgreSQL
-
This short article shows how to restart PostgreSQL in Ubuntu. Restart PostgreSQL Server in Ubuntu You can restart Postgres server in Ubuntu using the following command. Order: sudo service postgres restart Sometimes the above command does n
Issues to note when installing Apache on Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:78 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
As the most commonly used web server, Apache can be used in most computer operating systems. As a free and open source Unix-like operating system, Linux and Apache are a golden pair. This article will introduce the installation and use of A
How to decompress x.tar.xz format files under Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:186 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
A lot of software found today is in the tar.xz format, which is a lossless data compression file format that uses the LZMA compression algorithm. Like gzip and bzip2, it supports multiple file compression, but the convention is not to compr
Summary of vim common commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:115 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In Linux, the best editor should be vim. However, the complex commands behind vim's powerful functions also make us daunted. Of course, these commands do not need to be memorized by rote. As long as you practice using vim more, you can reme
Detailed explanation of command return value $? in Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:58 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
? is a special variable. This variable represents the return value of the previous command. That is to say, when we run certain commands, these commands will return a code after running. Generally, if the command is successfully run, the re
Common judgment formulas for Linux script shell
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:159 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In shell script programming, predicates are often used. There are two ways to use predicates, one is to use test, and the other is to use []. Let's take a look at how to use these two methods through two simple examples. Example 1 # test –
Shell script programming practice - specify a directory to delete files
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:98 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Usually, in Linux system we need to frequently delete some temporary files or junk files. If we delete them one by one manually, it will be quite troublesome. I have also been learning shell script programming recently, so I tried to write
Use of Linux command at - set time to execute command only once
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:158 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
This article mainly involves a knowledge point, which is the atd service. Similar to this service is the crond service. The functions of these two services can be similar to the two functional functions of javascript. Those who have learned
Use of Linux command crontab - loop execution of set commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:170 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Compared with at , which executes a command only once, crontab, which we are going to talk about in this article, executes the set commands in a loop. Similarly, the use of crontab requires the support of the crond service. The service is s

