Best way to merge a Git branch into Master
One of the most powerful features of git is branch creation and merging operations. Git allows users to create a new branch and merge them into the development code. This feature improves the development process workflow of multiple projects by encouraging more specific, smaller, and more refined tasks.
In this tutorial article, we will discuss different ways to merge a git feature branch into master.
The main advantage of git is its branching system. All the magic of GIT is on these branches! The master branch will have all the modifications. So the goal is not to make modifications directly on this branch, but to make modifications on other branches and after various tests, integrate them on the master branch.
In our tutorial, for simplicity, we assume that there are two branches, mastermaster and feature-1feature branches called . The master branch is the main branch that contains the production code, and the second branch is where modifications are performed or new features are implemented. Finally, if a feature or bug is approved, it will be merged into master.
Let's start with a real example to demonstrate the merge of two branches. First, we need the following.
Prerequisites
Create a repository on GitHub
You can create an initial repository according to the instructions in Github
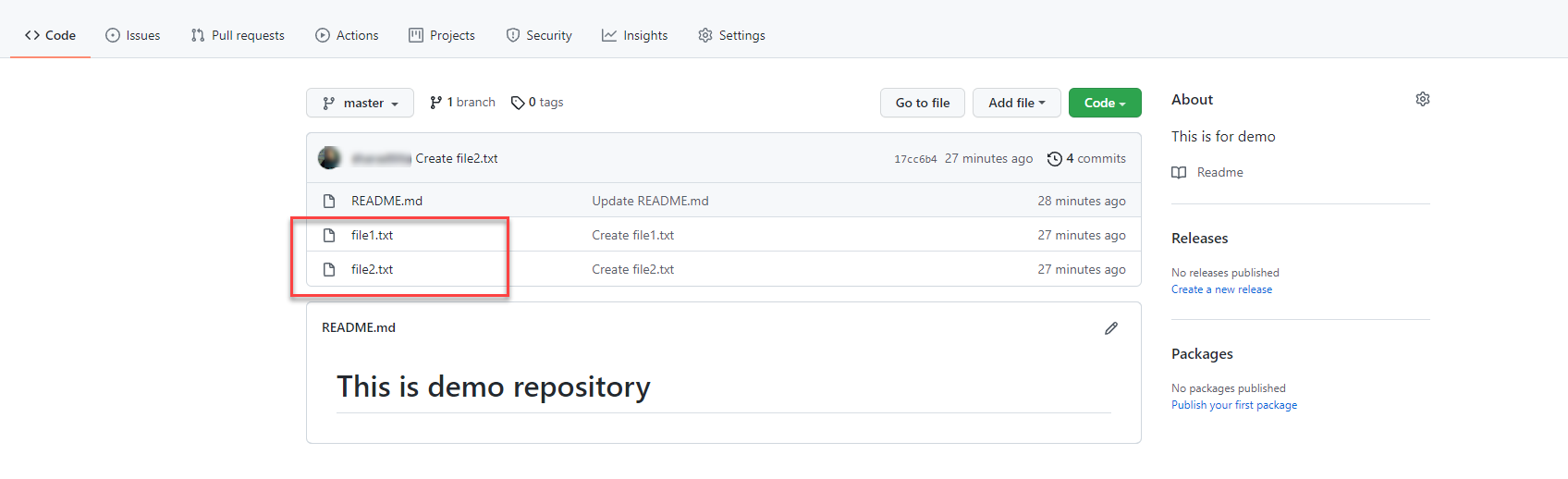
添加文件Next, add two files to the Master branch
using the buttons on the repository page . The file names are as follows.
-
file1.txt -
file2.txt
In this example, the following text content is added to file1.txtand respectively file 2.txt.
$ cat file1.txt
This is dummy text line 1
This is dummy text line 2
$ cat file2.txt
This is dummy test in 2nd file
Clone the repository
Next, clone your newly created repository from GitHub to your system to create a local copy of the code. The clone URL can 代码be retrieved from the button as shown below.
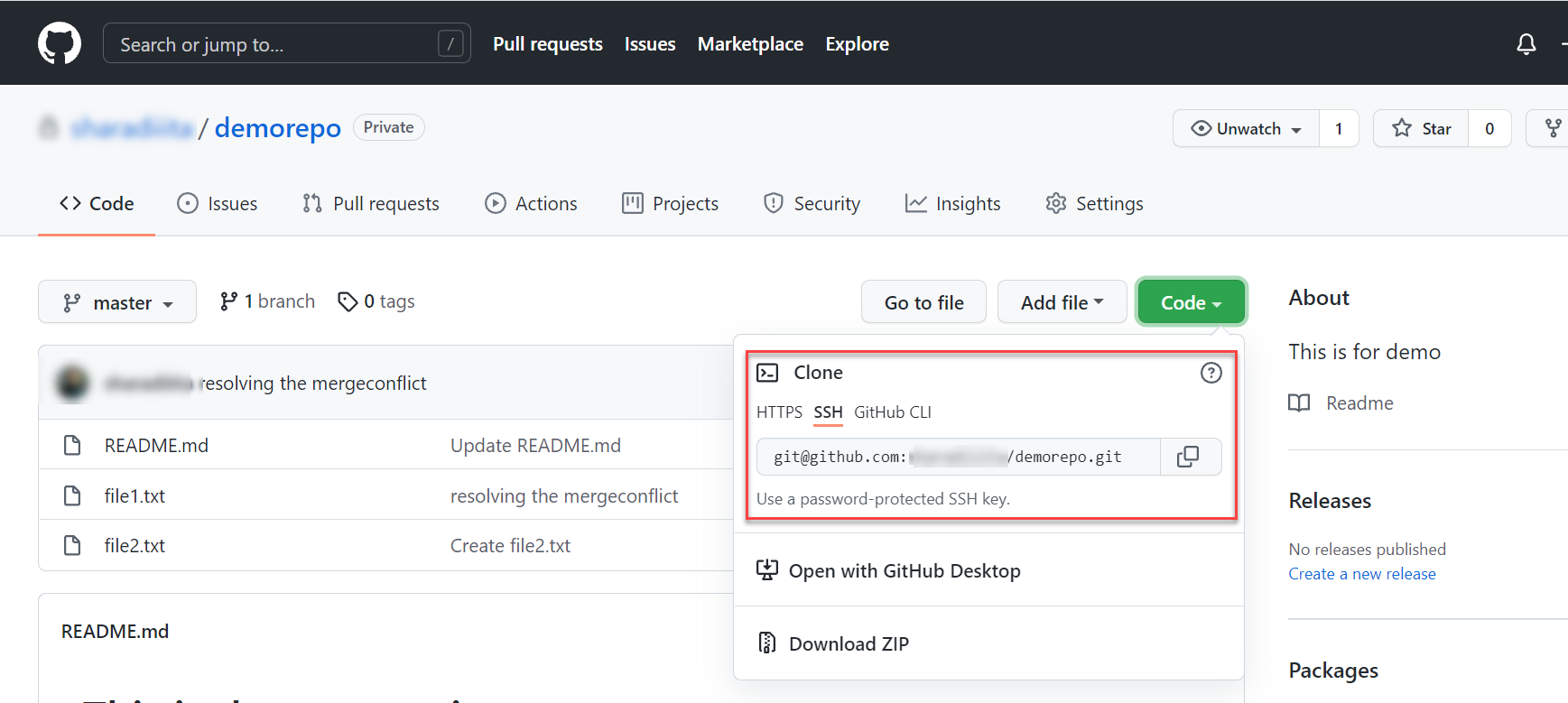
Use the following command to clone.
$ git clone git@github.com:project/demorepo.git
After cloning successfully, use the following command to display and verify the contents of the master branch file:
$ cat file1.txt
This is dummy text line 1
This is dummy text line 2
$ cat file2.txt
This is dummy test in 2nd file
Creating a feature branch
$ git branch feature-1
This command creates a new branch and does not create new commits on git.
Check out feature branch
Earlier, we git branch feature-1created a new branch using . However, the active branch is masterthe branch. To activate the new branch, use the following command in your terminal:
$ git checkout feature-1
Switched to branch 'feature-1'
The above command will switch the active branch from masterto feature-1. Now, this branch is ready for separate development.
Modify files in feature branches
We will feature-1make some commits or add new lines in the branch. In this case, file2.txtit will be modified locally and then merged back to the master branch.
For the changes so far, our commit graph looks like this. A and E both represent the masterand feature-1branch states. Currently, commits Aand Eare the same because no files were changed during the switch.
A ← master
\
E ← feature-1
Now, file1.txtupdate with the new text. Use this command to update the content.
$ echo "file update in feature branch" > file1.txt
Now, file2.txthave the following content.
$ cat file2.txt
This is dummy test in 2nd file
file1.txtThe difference between the old and new contents can be verified using the following command.
$ git diff
diff --git a/file1.txt b/file1.txt
index 11d66d4..48c9378 100644
--- a/file1.txt
+++ b/file1.txt
@@ -1,2 +1 @@
-This is dummy text line 1
-This is dummy text line 2
+file update in feature branch
Now, stage this file and create a local commit by the following command.
$ git add file1.txt
$ git commit -am "update file via feature-1"
[feature-1 22b60b8] update file via feature-1
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 2 d
The current snapshot of the commit tree is shown below. Here Fis the new commit created in the previous step.
A ← master
\
E --- F ← feature-1
To demonstrate a real example, the remote masteris also being changed concurrently by other developers, and these changes are pushed to master as commits Cand commits .D
A --- B --- C --- D ← master
\
E --- F ← feature-1
Here are file1.txtthe updates from the master branch of the Github repository. Note that line 2 has been updated, and lines 3 and 4 are newly created.
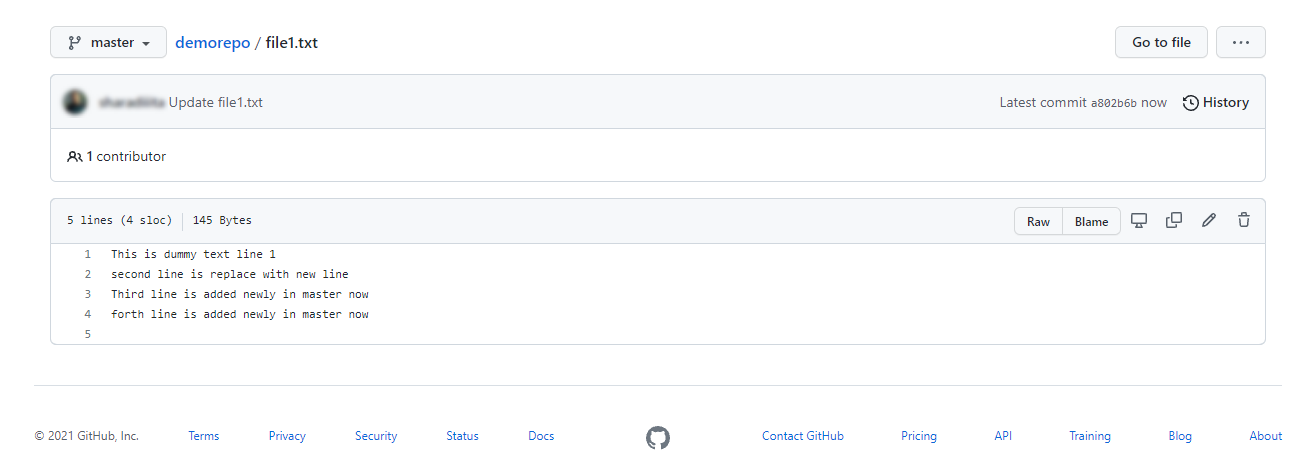
This can also be verified locally by visualizing your branch history in real time in a command shell using the following command.
$ git fetch
$ git log --all --decorate --oneline --graph
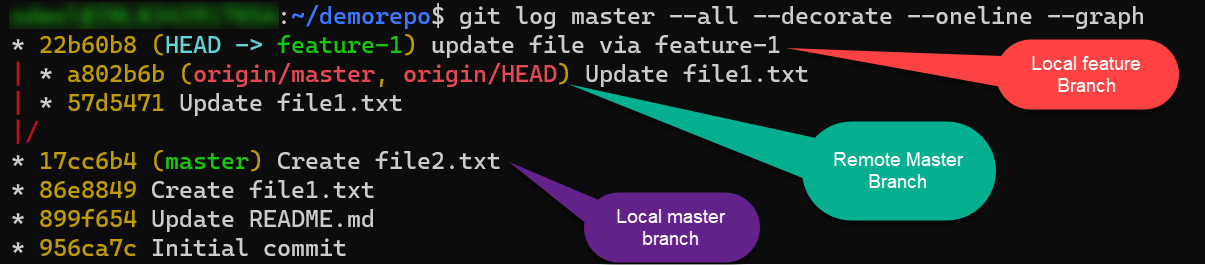
Preparing to merge in Git
Using Git, we have two possibilities to merge our feature branch changes with the remote masterbranch:
-
mergeMethod
Gitmergeis a command to commit changes to another branch. It allows developers to take their independent lines of code from feature branches and integrate them into a single branch on master through the git merge tool. -
rebaseMethod
Gitrebaseis another command that serves essentially the same purpose, except that it does it very differently.
Let’s look at both of these in detail:
Use the Git mergemethod to merge the branch into Master
mergeThe goal is to merge the featureand masterbranches into a commit that preserves the contents of all related branches. Git implements this with the so-called 合并提交. This also means mergeoperating on multiple branches.
When a branch diverges, i.e. one is not an ancestor of the other. Git can implement a merge by making a new additional commit with multiple parents. In the following diagram, if you have commits Dand commits in different branches Fand you merge the branches (via git merge), the result is a commit Gwhose parents are Band E.
A --- B --- C --- D ---
\ \
\ G ← master
E --- F --------- /
In the picture above, Gthere is a newly created commit, created entirely by git. This commit has two parents! They have a command:
-
The first parent node is
D, and the previous one ismaster. -
The second parent node is
F, and the previous one isfeature-1.
This type of commit is called a merge commit.
Now switch back to our example repository and feature-1merge the newly created branch intomaster
First, check out the master branch.
$ git checkout master
Now, pull the remote masterchanges to your local one master.
$ git pull origin master
From github.com:repo/demorepo
* branch master -> FETCH_HEAD
Updating 17cc6b4..a802b6b
Fast-forward
file1.txt | 5 ++++-
1 file changed, 4 insertions(+), 1 deletion(-)
After that, merge the feature branch i.e. feature-1into the currently active branch using the following command.
$ git merge feature-1
If this step completes successfully, feature-1your branch will be fully merged with masteryour branch. However, if git cannot automatically resolve these merge conflicts, it will fail with a merge conflict error.
This is a very typical scenario; it happens when two branches modify the same part of a file and git can't resolve which part to use. This is exactly what happened in our example. Below is a display of this happening with git.
Auto-merging file1.txt
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in file1.txt
Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
Whenever git encounters a conflict, it adds <<<<<<<& ========to highlight the part that caused the conflict, which needs to be resolved manually.
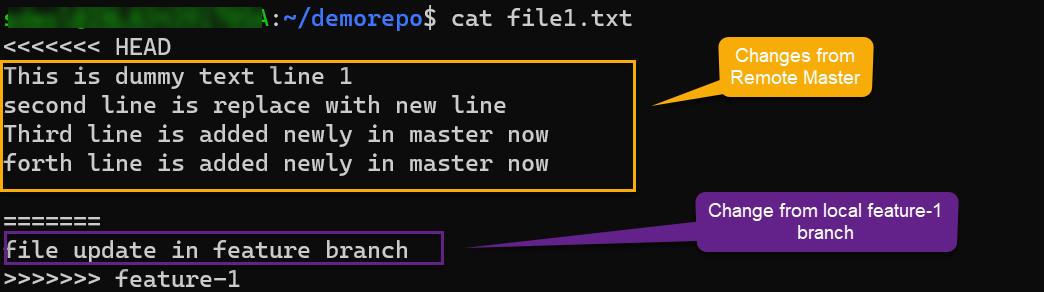
Once you decide which part to keep in the final master version of the file, you must remove the irrelevant code (including the conflict indicators). Finally, push the changes to the remote branch as shown below.
$ git add .
$ git commit -am "resolving the mergeconflict"
[master 1acce69] resolving the mergeconflict
$ git push
This feature-1branch is successfully merged to the remote master.
Next, we will verify the branch history again using the following command.
git log --all --decorate --oneline --graph
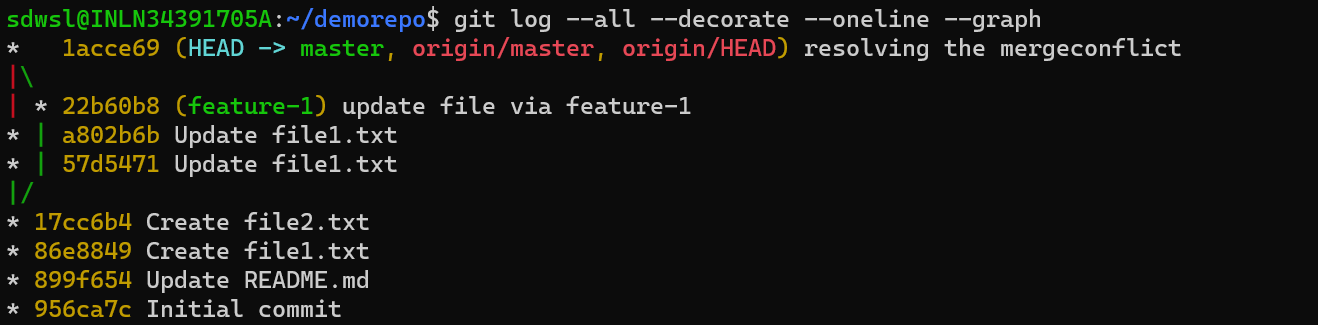
We can verify mergethat git created a Merge Commitcommit-id 1acce69to merge feature-1the branch with origin/master.
Use rebasethe method to merge the branch into Master
Consider again the situation where our feature and master branches are out of sync and need to be merged. Let's also revisit the previous diagram that shows this situation.
A --- B --- C --- D ← master
\
E --- F ← feature-1
As an alternative to merging, you can feature-1merge branch into branch using the rebase option master. rebaseThis unifies the branches involved by simply putting the commits from the feature branch in front of the master branch.
This will be achieved with the following command,
git checkout master
git pull
git checkout feature-1
git rebase master
After running rebase, we can get the following figure.
A --- B --- C --- D----(operation rebase)----- E--------F ← master
As you can see from the above diagram, rebasesome of the good things this does is produce a linear, cleaner, easier to read commit history. It also doesn't create additional weirdness through the merge merge commit.
The disadvantage of this approach is that rebase changes the entire structure of the branches involved, including rewriting the commit history of those branches. Since rebaseis not created merge commit, you cannot get traceability of when two branches merged, because rebase produces a linear branch at the end of the process.
in conclusion
Both commands are very useful; however, each has advantages in different situations.
Gitrebase
- Simplifying complex history.
- Avoid merge commit noise in repositories with busy branches.
- It is risky if used incorrectly as it does not preserve history.
Gitmerge
- Easy to use.
- Since an additional merge commit is created each time, it causes the commit history to look messy and dirty.
- Keep the complete history and chronology.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Git installation and establishment of local warehouse service
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:89 Category:Git
-
Git is a distributed version control system: the client does not only extract the latest version of the file snapshot, but also completely mirrors the original code repository. It has the following advantages: a. Since every extraction oper
git remote operation——multiple remote repositories for one project
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:131 Category:Git
-
Multiple remote repositories for a git project In our git project, the command to operate the remote repository information is $ git remote # 查看当前所有的远程仓库的名称 $ git remote -v # 查看远程仓库的名称和远程仓
Git cherry pick command usage
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:190 Category:Git
-
git cherry-pick is a powerful command that allows us to select an arbitrary Git commit by reference and attach it to the HEAD of the current working branch. Cherry picking is the act of picking a commit from one branch and applying it to an
Comparison between Git merge and Git rebase
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:171 Category:Git
-
The git rebase command may seem like Git wizardry to beginners, but if used carefully, it can actually make life easier for your development team. In this article, we compare git rebase with the related git merge command and identify all th
How to fix Git error Error: src refspec master does not match any
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:124 Category:Git
-
When using Git, we may encounter the error "src refspace master does not match any". Here's what the error means and how to fix it. What does src refspec master does not match any Mean in Git mean? We may encounter this error when we try to
Rebase local branch when pulling changes from remote repository branch in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:144 Category:Git
-
This article will cover the basics of rebasing your local branch when pulling changes from a remote repository branch in Git. We use the version control system Git to track changes made to files. We commit changes in a local branch in our l
Undo Git Stash
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:187 Category:Git
-
This article explains how to make and save changes to a repository. Git allows you to save changes locally and push them to a server when needed. In Git, we don't use the term save , but commit . We use git add , git commit , and git stash
View a list of cache entries in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:59 Category:Git
-
We often need to pause our work and focus on something else in our development environment. Therefore, we may need to temporarily save our current work and focus on a different one. We may want to resume our original work later. git stash T
Git stores specific files
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:115 Category:Git
-
This article will cover storing changes to only specific files in Git. In Git, when we make some changes in our working tree, we may have some changes which may or may not be staged in our local repo. We may now wish to save these changes f

