Using Git Rebase from the Command Line
This article will discuss using the git rebase command effectively . The git rebase command allows us to change a range of commits and modify the commit history in our repository.
We can edit, reorder, or squash commits using the git rebase command.
Using git rebase from the command line
Here are some common usage options.
- We can edit previous commit messages.
- We can merge two or more commits into one.
- We can revert or delete unnecessary commits in the repository.
When rebasing, we can rebase against a branch or a point in time in the repository.
To rebase against a branch, we run:
$ git rebase --interactive <branch_name>
To rebase to a point in time, we run:
$ git rebase --interacive HEAD~
We can add HEAD~7 to rebase to the seventh commit.
Let's look at the commands available when rebasing.
- pick - We use this to reorder our commit history.
- reword − It is used when we want to change the commit message. It does not affect the changes introduced by the commit.
- edit − It is used when we want to edit or modify a commit. We can split the commit into smaller commits or remove the errors introduced by the commit.
- squash - We use this to merge two commits into one and gives us the opportunity to provide a new message for the new commit.
- fixup - It is the same as squash, except that it discards the merge commit's message and uses the message above it.
We will now try to use the above options in an example. In this example, we will rebase against a point in time in the Delftscopetech repository.
We will rebase HEAD~7 . Run the following command:
$ git rebase --interactive HEAD~7
The text editor displays the following output.
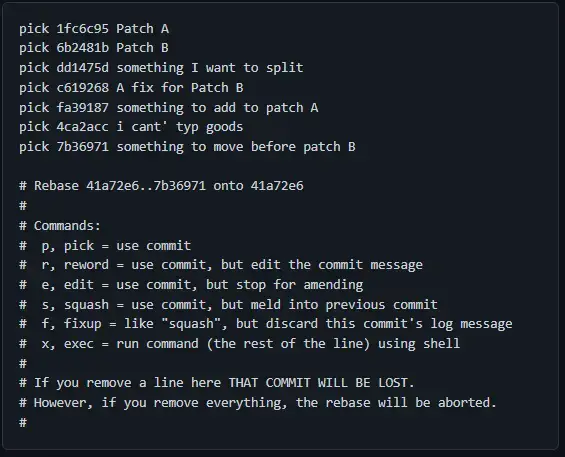
Our commits are sorted from oldest to newest.
In our text editor we will:
- Use squash to squash commit (fa39187) into commit (1fc6c95).
- Move the last commit (7b36971) before commit (6b2481b) and keep it as pick.
- Merge commit (c619268) into commit (6b2481b) with fix-drop commit message.
- Use Edit Split (dd1475d).
- Fix the commit message using reword (4ca2acc).
We will modify the command in the text editor as shown below.
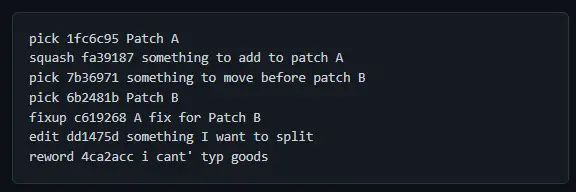
We can save and close our text editor, and Git will start the rebase.
Git will skip picking 1fc6c95 and open an editor because squash needs some input from us. It should look something like this.
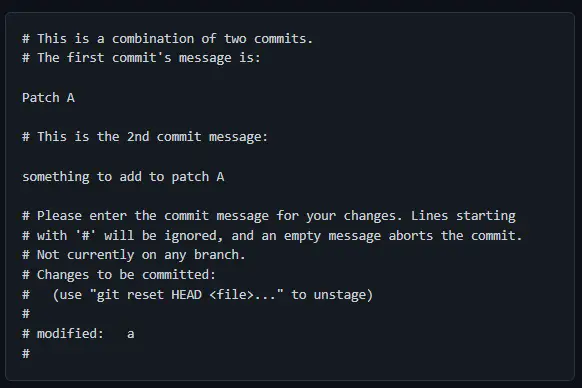
If you are happy with the changes, you can close the editor and continue with the rebase. The next three commands require no input from us, but the editor does and will print the following messages to the terminal.
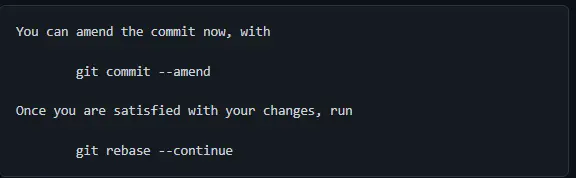
At this point, we can make any changes and create a new commit using the git commit --amend command. Once we are done, we can continue by running the git rebase --continue command.
Always run git rebase --continue after making changes. If you forget to run the command and continue coding, you won't be able to rebase later.
However, you can remedy this by:
-
Run
git reset --soft HEAD^the command to ref HEAD to the parent. -
Run
git rebase --continueto complete the rebase.
You can also abort the rebase and redo the process by running the git rebase --abort command. This will require you to resolve the merge conflicts again.
The rewrite section will require our input and Git will open the text editor with the following information.
We can change the text, save the file and complete the rebase.
In short, the git rebase command allows us to change the state of a repository based on commits. We can squash, rename, or reorder commits.
Be careful when rebasing and there are merge conflicts.
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
Git installation and establishment of local warehouse service
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:89 Category:Git
-
Git is a distributed version control system: the client does not only extract the latest version of the file snapshot, but also completely mirrors the original code repository. It has the following advantages: a. Since every extraction oper
git remote operation——multiple remote repositories for one project
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:131 Category:Git
-
Multiple remote repositories for a git project In our git project, the command to operate the remote repository information is $ git remote # 查看当前所有的远程仓库的名称 $ git remote -v # 查看远程仓库的名称和远程仓
Git cherry pick command usage
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:190 Category:Git
-
git cherry-pick is a powerful command that allows us to select an arbitrary Git commit by reference and attach it to the HEAD of the current working branch. Cherry picking is the act of picking a commit from one branch and applying it to an
Comparison between Git merge and Git rebase
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:171 Category:Git
-
The git rebase command may seem like Git wizardry to beginners, but if used carefully, it can actually make life easier for your development team. In this article, we compare git rebase with the related git merge command and identify all th
How to fix Git error Error: src refspec master does not match any
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:124 Category:Git
-
When using Git, we may encounter the error "src refspace master does not match any". Here's what the error means and how to fix it. What does src refspec master does not match any Mean in Git mean? We may encounter this error when we try to
Rebase local branch when pulling changes from remote repository branch in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/05 Views:144 Category:Git
-
This article will cover the basics of rebasing your local branch when pulling changes from a remote repository branch in Git. We use the version control system Git to track changes made to files. We commit changes in a local branch in our l
Undo Git Stash
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:187 Category:Git
-
This article explains how to make and save changes to a repository. Git allows you to save changes locally and push them to a server when needed. In Git, we don't use the term save , but commit . We use git add , git commit , and git stash
View a list of cache entries in Git
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:59 Category:Git
-
We often need to pause our work and focus on something else in our development environment. Therefore, we may need to temporarily save our current work and focus on a different one. We may want to resume our original work later. git stash T
Git stores specific files
Publish Date:2025/04/04 Views:115 Category:Git
-
This article will cover storing changes to only specific files in Git. In Git, when we make some changes in our working tree, we may have some changes which may or may not be staged in our local repo. We may now wish to save these changes f

