Bash variable scope
In this article, we will learn about bash variable scope in Linux. We also learned how to declare variables in bash scripts in Linux operating system.
Furthermore, we will see different types of variables and how to access local and global variables in bash scripts using Linux operating system. Let us start with the concept of variables used in Linux.
Bash variable scope in Linux
A variable is a temporary storage space for various data types handled in any programming language. A variable is usually associated with two separate entities: the data type and its value.
The data type describes the data stored in the variable, whereas the value represents the data itself. While declaring a variable in Bash programming, we do not need to explicitly specify the data type.
This is because the programming language itself detects the data type. For example, in bash, if we assign a number to a variable, it is immediately treated as an integer.
How to declare variables in Bash
In bash, we can declare a variable with any name using the equal sign "=" and the value we want to assign. Here are some rules we can follow when declaring variables in bash:
- Uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, underscores, and decimals are all acceptable characters for variable names.
- It is recommended to use uppercase letters for variable names in Bash scripts.
- Do not put spaces around the equal sign "=".
- All predefined keywords are restricted, such as if, else, local, etc.
Following is an example of declaring a String variable in bash. We open the terminal and declare the variable. Don't forget that while declaring the variable, we are not allowed to put any spaces around the equal sign ('=').
$ _name=abid
We use echoto get the output of the variable.
$ echo $_name
Output:
abid
Declare an integer variable in bash.
$ _age=24
Similarly, using echo, we can also get the output of this variable.
$ echo $_age
Output:
24
Variable scope in Bash
The scope of Bash variables can be local or global, just like in any other programming language. It does not matter where they are declared in our Bash script.
By default, all variables in bash have global scope. This means that the variable can be used inside any function in the bash script, even if it is defined in the middle of the script.
In other words, we might argue that in bash we don't always have to declare a variable at the beginning of a script to make its scope global.
Furthermore, if we want the scope of that variable to be limited to a specific function, we must explicitly use the local keyword when declaring a variable in bash, which means that no other functions in that script or anywhere else can access it.
This will ensure that the scope of the variable is limited to the function in which it is defined.
Variable Types
There are three main types of variable scopes we need to know about.
- Local variables
- Global variables
- Environment variables
Accessing local variables in Bash
We can access local variables only within the code block they are declared in. For example, if we declare a variable inside a Bash script, we will not be able to access it outside the code.
Sample code:
#!/bin/bash
echo "Learning the scope of local and global variables."
function_localVar(){
echo "Within the function function_localVar"
echo "Assign a variable with local keyword to a variable name: varLocal"
local varLocal=27
echo "Assign a variable without local keyword to a variable name: varLocal_wo"
varLocal_wo=9
echo "Printing within the function."
echo "Value assigned to one with local keyword varLocal = $varLocal and without local keyword varLocal_wo = $varLocal_wo"
echo "Exiting function_localVar"
}
glob_var=91
echo "Start of the code!"
echo "Global Variable = $glob_var"
echo "Local variable before calling function to one with local keyword varLocal = ** $varLocal ** and without local keyword varLocal_wo = ** $varLocal_wo **"
echo "Calling the function."
function_localVar
echo "Printing outside the function."
echo "Value assigned to one with local keyword varLocal = $varLocal and without local keyword varLocal_wo = $varLocal_wo"
Output:
Learning the scope of local and global variables.
Start of the code!
Global Variable = 91
Local variable before calling function to one with local keyword varLocal = ** ** and without local keyword varLocal_wo = ** **
Calling the function.
Within the function function_localVar
Assign a variable with local keyword to a variable name: varLocal
Assign a variable without local keyword to a variable name: varLocal_wo
Printing within the function.
Value assigned to one with local keyword varLocal = 27 and without local keyword varLocal_wo = 9
Exiting function_localVar
Printing outside the function.
Value assigned to one with local keyword varLocal = and without local keyword varLocal_wo = 9
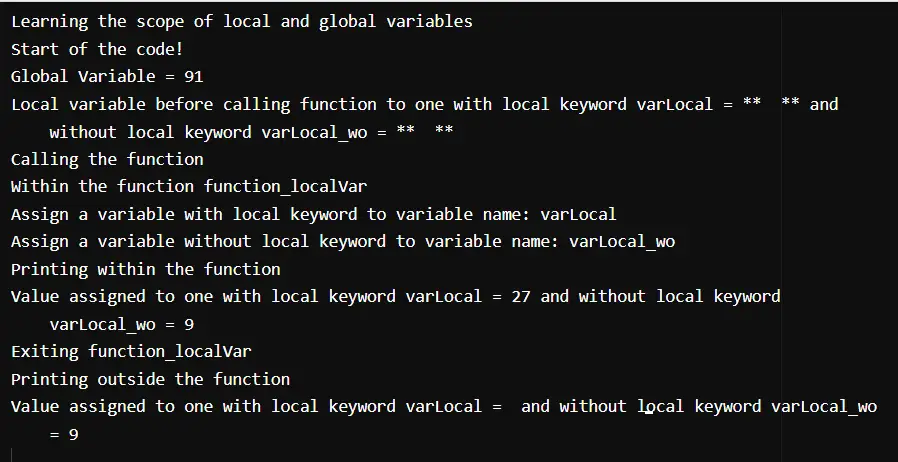
From the following code, it is clear that, may be the local keyword sets the scope to local, even when the variable is read outside the function defined as local, it returns null.
Accessing Global Scope Variables in Bash
We can access global variables throughout the bash script. The following example helps us understand how global variable scope works in bash.
Sample code:
var1='Abid'
var2='Ali'
my_function () {
local var1='Micheal'
var2='Den'
echo "Inside function: var1: $var1, var2: $var2"
}
echo "Before executing the function: var1: $var1, var2: $var2"
my_function
echo "After executing the function: var1: $var1, var2: $var2"
Output:
Before executing the function: var1: Abid, var2: Ali
Inside function: var1: Micheal, var2: Den
After executing the function: var1: Abid, var2: Den
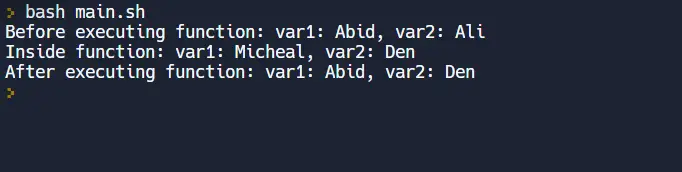
The results of the above code lead us to the following conclusions:
- Whenever you set a local variable in function scope with the same name as an existing global variable, the local variable will take precedence.
- It is indeed possible to make changes to global variables from within a function.
Environment variables
Environment variables (ENV) essentially specify how the environment works. In bash, environment variables can have global or local scope.
We can access the globally scoped ENV generated in the terminal from anywhere in the terminal environment. Because it runs in the context of the terminal, it can be used in any script, program or process.
Any application or process executed in the terminal cannot access the local scope ENV specified there. Only the terminal in which we define the variable can access it.
Setting Environment Variables
As an environment variable at global scope:
$ export COUNTRY=USA
# 或者
$ set NAME=Abid
As a locally scoped environment variable:
$ NAME=Abid
Now, the point is how to display environment variables. We can use to echodisplay environment variables like normal variables.
$ echo $COUNTRY
Output:
USA
The output of this command will be the value we assigned to this variable COUNTRY, which is USA.
Display all environment variables
We can display all ENV using three different commands.
-
Only used to display all global environment variables
$ printenv -
We use this command to display local and global environment variables
$ set -
Used to display all global environment variables
$ env
For reprinting, please send an email to 1244347461@qq.com for approval. After obtaining the author's consent, kindly include the source as a link.
Related Articles
How to decompress x.tar.xz format files under Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:186 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
A lot of software found today is in the tar.xz format, which is a lossless data compression file format that uses the LZMA compression algorithm. Like gzip and bzip2, it supports multiple file compression, but the convention is not to compr
Summary of vim common commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:115 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In Linux, the best editor should be vim. However, the complex commands behind vim's powerful functions also make us daunted. Of course, these commands do not need to be memorized by rote. As long as you practice using vim more, you can reme
Detailed explanation of command return value $? in Linux
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:58 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
? is a special variable. This variable represents the return value of the previous command. That is to say, when we run certain commands, these commands will return a code after running. Generally, if the command is successfully run, the re
Common judgment formulas for Linux script shell
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:159 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
In shell script programming, predicates are often used. There are two ways to use predicates, one is to use test, and the other is to use []. Let's take a look at how to use these two methods through two simple examples. Example 1 # test –
Shell script programming practice - specify a directory to delete files
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:98 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Usually, in Linux system we need to frequently delete some temporary files or junk files. If we delete them one by one manually, it will be quite troublesome. I have also been learning shell script programming recently, so I tried to write
Use of Linux command at - set time to execute command only once
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:158 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
This article mainly involves a knowledge point, which is the atd service. Similar to this service is the crond service. The functions of these two services can be similar to the two functional functions of javascript. Those who have learned
Use of Linux command crontab - loop execution of set commands
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:170 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Compared with at , which executes a command only once, crontab, which we are going to talk about in this article, executes the set commands in a loop. Similarly, the use of crontab requires the support of the crond service. The service is s
Linux practice - regularly delete files under the directory
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:198 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Since we want to delete the files under the directory regularly, we need to use the Linux crontab command. And the content format of each work routine is also introduced in the format of each crontab work. Similarly, we need to use shell sc
How to use the Linux file remote copy command scp
Publish Date:2025/04/08 Views:151 Category:OPERATING SYSTEM
-
Scp copies files between two hosts over the network, and the data is encrypted during transmission. Its underlying layer uses ssh for data transmission. And it has the same authentication mechanism and the same security level as ssh. When u

